
Light of wavelength 550nm falls normally on a slit of width 22.0×10 −5cm.Unpolarized light of intensity I is incident on a system of two polarizers, A followed by B…?.(ii) If the monochromatic source of ligght is replaced by a white light, instead of white fringes we will have coloured fringes on either side of the central white fringe and then uniform illumination on the screen. (b) (i) For the given monochromatic waves, if the width of the slit is decreased, the fringe pattern becomes broader. Thus, net contribution from the two halves is zero and with that intensity falls to zero for path difference, Δ = nλĬondition for maxima: If slit AB is parted into three equal halves and if two thirds of the slit having a path difference λ/2 between them cancel each other and only the remaining one third of the set contributes to the intensity at the point between two minima, so the path difference, Δ =(n +1/2)λ (5 marks)Ĭondition for minima: If the set AB is parted into equal halves each of size d/2, for every point in part AM, there is a point in part MB that contributes the secondary wavelets out of phase. (ii) the monochromatic source of light is replaced by a white light. (b) How would the diffraction pattern be affected when Derive the conditions when secondary wavelets originating from the slit interfere to produce maxima ans minima on the screen. Ques 15) (a) A monochromatic source of light of wavelength λ illuminates a narrow slit of width d to produce a diffraction pattern on the scree. On the other hand, in a diffraction pattern, the fringes are of different widths. In interference pattern, the width of all fringes are almost the same.Whereas, in the diffraction pattern, all the dark fringes are not of zero intensity. The dark fringes have zero or small intensity so that the bright and dark fringes can be easily distinguished in the interference pattern.The bright fringes are not of the same intensity in the single slit diffraction pattern. All the bright fringes have the same intensity in the interference pattern.The three distinguishing features that are observed in Young’s double slit experiment when compared to single slit diffraction pattern are, The maxima between the minima and the width of the central maximum is simply the distance between the 1st order minima from the centre of the screen on both sides of the centre.Īns.Single Slit Diffraction is that which produces refraction, interference, diffraction, reflection, etc when light travels in the air.It is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limited or finite distance from the diffracting system. Fresnel Diffraction occurs due to size of the obstruction.Fraunhofer Diffraction is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limitless or infinite distance from the diffracting system.Diffraction is chiefly of two types - Fraunhofer Diffraction and Fresnel Diffraction.Diffraction occurs with all waves which include water waves, sound waves, electromagnetic waves.The phenomena of diffraction can be observed if the size of the opening is relative to the size of the wavelength of light.Diffraction of light is defined as the slight bending of light waves around the border of a slit or an object.Diffraction object gives rise to wavefronts that are also straight or plane.ĭifference between Diffraction and InterferenceĬoherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves.
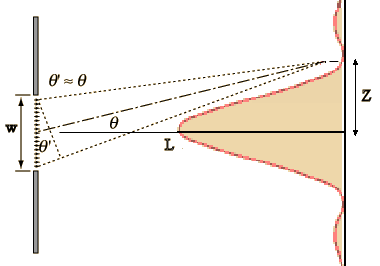
To produce a diffraction pattern, the plane or horizontal wavefront is connected by means of a convex lens.The incident wavefronts on the diffracting obstacle are horizontal or plane.The screen and the source are infinite from each other.The important points for Fraunhofer Diffraction are discussed in the below points:

Fraunhofer Diffraction occurs when the distance is increased and the outgoing diffracted wave becomes straight or horizontal. By using a convex lens, the diffraction pattern is obtained. Resolving Power of Microscopes and Telescopesĭiffraction is primarily categorized into two types -įraunhofer Diffraction is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limitless or infinite distance from the diffracting system. Transmission, Absorption and Reflection of Light Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
